The Government of Canada (French: Gouvernement du Canada) is the body responsible for the federal administration of Canada. The term Government of Canada refers specifically to the executive, which includes ministers of the Crown (together in the Cabinet) and the federal civil service (whom the Cabinet direct); it is alternatively known as His Majesty’s Government (French: Gouvernement de Sa Majesté) and is corporately branded as the Government of Canada. There are over 100 departments and agencies, as well as over 300,000 persons employed in the Government of Canada. These institutions carry out the programs and enforce the laws established by the Parliament of Canada.
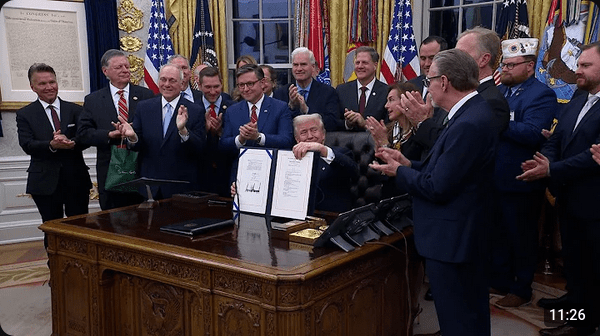
The federal government’s organization and structure was established at Confederation, through the Constitution Act, 1867, wherein the Canadian Crown acts as the core, or “the most basic building block”, of its Westminster-style parliamentary democracy. The monarch, King Charles III is head of state and is personally represented by a governor general (currently Mary Simon). A prime minister (currently Justin Trudeau) is the head of government, who is invited by the Crown to form a government after securing the confidence of the House of Commons, which is typically determined through the election of enough members of a single political party in a federal election to provide a majority of seats in Parliament, forming a governing party. Further elements of governance are outlined in the rest of the Canadian constitution, which includes written statutes in addition to court rulings and unwritten conventions developed over centuries.
Constitutionally, the King’s Privy Council for Canada is the body that advises the sovereign or their representative on the exercise of executive power. This task is carried out nearly exclusively by the Cabinet, which functions as the executive committee of the Privy Council that sets the government’s policies and priorities for the country and is chaired by the prime minister. The sovereign appoints the members of Cabinet on the advice of the prime minister who, by convention, are generally selected primarily from the House of Commons (although often include a limited number of members from the Senate). During its term, the government must retain the confidence of the House of Commons and certain important motions, such as money bills and the speech from the throne, are considered as confidence motions. Laws are formed by the passage of bills through Parliament, which are either sponsored by the government or individual members of Parliament. Once a bill has been approved by both the House of Commons and the Senate, royal assent is required to make the bill become law. The laws are then the responsibility of the government to oversee and enforce.