Central Bank of Sri Lanka
The Central Bank of Sri Lanka (abbr. CBSL; Sinhala: ශ්රී ලංකා මහ බැංකුව, romanized: Sri Lanka Maha Bankuwa) is the monetary authority of Sri Lanka. It was established in 1950 under the Monetary Law Act No.58 of 1949 (MLA) and in terms of the Central Bank of Sri Lanka ActSpider

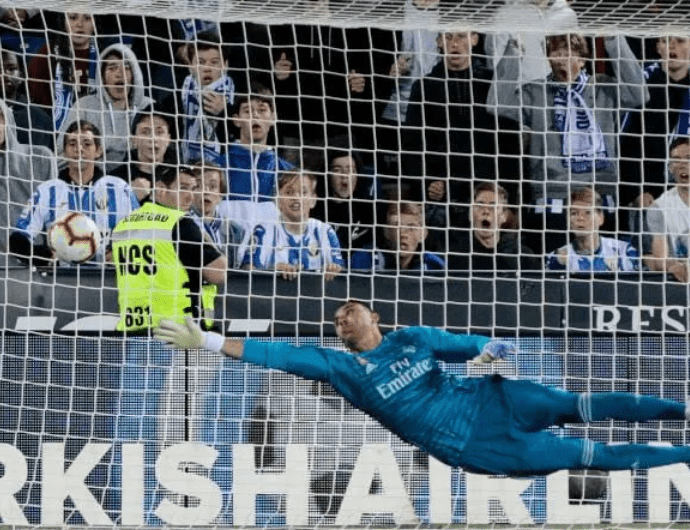
 Kings League Spain – JORNADA 9
Kings League Spain – JORNADA 9  #KINGSLEAGUEJ9
#KINGSLEAGUEJ9

















































































































































 | #WorldSBK
| #WorldSBK





 [Live] เกาะติดพื้นที่อาคารสูงย่านจตุจักร หลังแผ่นดินไหว กทม. | ไลฟ์วันนี้ | 28 มี.ค.68
[Live] เกาะติดพื้นที่อาคารสูงย่านจตุจักร หลังแผ่นดินไหว กทม. | ไลฟ์วันนี้ | 28 มี.ค.68









































 国会中継 衆議院 本会議(2025/03/25)
国会中継 衆議院 本会議(2025/03/25)






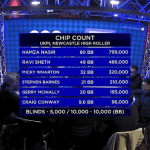
 Final Day of €165 Polish Poker Masters NLH Mystery Bounty live from King’s Resort
Final Day of €165 Polish Poker Masters NLH Mystery Bounty live from King’s Resort 












































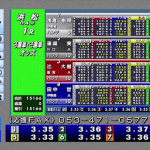



















































































































































 押忍!番長3!
押忍!番長3! 
























































































 】成田空港から快適な家族旅行を
】成田空港から快適な家族旅行を (なるほど☆成田空港/前編)】
(なるほど☆成田空港/前編)】



























































 Ca$h King$ Special “KingKhan’s” Game €25/€25 PLO Cash Game live from King’s Resort
Ca$h King$ Special “KingKhan’s” Game €25/€25 PLO Cash Game live from King’s Resort 



































 ライトニングバカラを生配信♠️軍資金を倍にできると、、、
ライトニングバカラを生配信♠️軍資金を倍にできると、、、


































 賞金総額7500万
賞金総額7500万




















 Watch
Watch Weather Check
Weather Check










 進化して帰ってきた簡単予想を公式Vチューバー、九院姫乃が解説
進化して帰ってきた簡単予想を公式Vチューバー、九院姫乃が解説



















 Day 3 of €380 Italian Poker Sport Main Events live from King’s Resort
Day 3 of €380 Italian Poker Sport Main Events live from King’s Resort 


















































































































































































 くいかじ公式Vチューバーの麻雀解説動画
くいかじ公式Vチューバーの麻雀解説動画






















































































































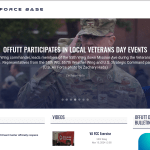
 US soldiers
US soldiers






























































 Day 3 of €1.100 WSOP Circuit NLH Main Events (Ring #10) live from King’s Resort
Day 3 of €1.100 WSOP Circuit NLH Main Events (Ring #10) live from King’s Resort 

































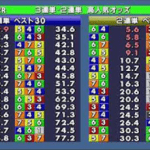










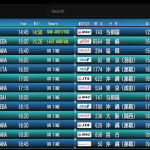














































































 Pazuru パズルカジノ!オンライン競馬の新たな魅力に迫る!
Pazuru パズルカジノ!オンライン競馬の新たな魅力に迫る!























 Trend by @cosme
Trend by @cosme















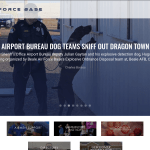
 soldiers train NATO Allies in winter survival skills
soldiers train NATO Allies in winter survival skills



























































 Navidad 2024 en Aeropuerto #JorgeChávez
Navidad 2024 en Aeropuerto #JorgeChávez 












































































































 DMMオンラインクレーンゲーム
DMMオンラインクレーンゲーム



 2025年 新春あけおめ企画!パズくじで$1888ボーナスをゲット!Pazuru パズルカジノ
2025年 新春あけおめ企画!パズくじで$1888ボーナスをゲット!Pazuru パズルカジノ









































 Czech Poker Masters Christmas Edition Main Event live from King’s Resort
Czech Poker Masters Christmas Edition Main Event live from King’s Resort 




























 (Ft. Michael Kopech and Ryan Pepiot)
(Ft. Michael Kopech and Ryan Pepiot)

























 Check
Check





















































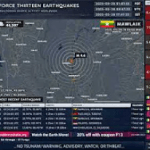
 Tsunami
Tsunami Pipeline Cam powered by EXPLORE.org
Pipeline Cam powered by EXPLORE.org








































































































 Check🕱
Check🕱























































 Chat
Chat DXLIVE
DXLIVE Event Information
Event Information










 Chat
Chat































































 Cosplay
Cosplay
 News Paper Magazine
News Paper Magazine









































































































 AV女優イベントスケジュールカレンダー
AV女優イベントスケジュールカレンダー




 Final Day of €1.100 “The Big Wrap” PLO 1k Mystery Bounty Event live from King’s Resort
Final Day of €1.100 “The Big Wrap” PLO 1k Mystery Bounty Event live from King’s Resort 


































































































 | November 1, 2024
| November 1, 2024







 Weather Map
Weather Map